# Introduction to Virtualization 0 # By SilentMing Blog: http://silentming.net [Slides](https://silentming.net/BlogExamples/virtualization-intro/virtualization-intro-0-slides.html#1) <!-- more --> --- ## Story Line ## * Brief introduction to virtualization * (Definition, histroy ...) * Classification * (Spectrum) * Architecture on ARM (Type-2 Hypervisor) * (It's simple, but only cover partial) --- ## What is Virtualization ## **Virtualization:** A layer mapping its visible interface and resources onto the interface and resources of the underlying layer or system on which it is implemented - Abstraction – to simplify the use of the underlying resource (e.g., by removing details of the resource’s structure) - Replication – to create multiple instances of the resource (e.g., to simplify management or allocation) - Isolation – to separate the uses which clients make of the underlying resources (e.g., to improve security) --- ## How Dose It Come ? ## Run **multiple OSes** on a **Single** Computer Histroy - 1960: [CP-40](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IBM_CP-40) - full virtualization - 1970: [System/370](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IBM_System/370) - without virtual memory, time-sharing - 1999: [VMware Virtual Platform](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X86_virtualization) - x86 virtualization support - 2003: [Xen and the Art of Virtualization](http://www.cs.yale.edu/homes/yu-minlan/teach/csci599-fall12/papers/xen.pdf) - Para-virtualization - 2005: [QEMU(Quick Emulator)](https://www.usenix.org/legacy/event/usenix05/tech/freenix/full_papers/bellard/bellard_html/) - rescue for those times when VMware is overkill - 2005: Free Desktop Virtualization - VMWare - 2005 & 2006: [Intel VT-x & AMD-V](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X86_virtualization) (Hardware support for virtualization) - 2007: [KVM(Kernel-based Virtual Machine)](https://ols.fedoraproject.org/OLS/Reprints-2007/OLS2007-Proceedings-V1.pdf#page=225) - 2011: [ARMv8](https://www.arm.com/files/downloads/ARMv8_white_paper_v5.pdf) virtualization support - 2013: [QEMU 1.5] ARM Cortex-A9 & Cortex-A15 - 2014: [KVM/ARM](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2541946) & [Xen 4.4](https://wiki.xenproject.org/wiki/Xen_Project_4.4_Feature_List) - 2017: [ARMv8.4: VHE(Virtualization Host Extension)](https://lwn.net/Articles/650524/) --- ## Why Virtualization ## #### Consolidation - Run several different OS on a single machine #### Isolation - Keep the VMs separated as error container - Fault tolerant #### Maintenance - Easy to deploy, backup, clone, (live) migrate #### Security - VM introspection (VMI) - Antivirus out of the OS --- ## Definition ## > The act of creating a **virtual (rather than actual) version of something**, including virtual computer hardware platforms, storage devices, and computer network resources. (wiki) > **A layer mapping** its visible interface and resources onto the interface and resources of the underlying layer or system on which it is implemented (CMU) > An enfficient, isolated **duplicate of the real machine** ([Formal Requirements for Virtualizable Third Generation Architectures](http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.141.4815&rep=rep1&type=pdf)) - Efficiency - Innocuous instructions should execute directly on hardware - Resource control - Executed programs may not affect the system resources - Equivalence - The behavior of a program executing under the VMM should be the same as if the program were executed directly on the hardware (except possibly for timing and resource availability) --- ## Basic Concepts ## 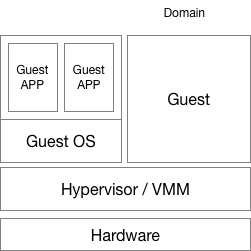 * Domain/VM (Virtual Machine) * Guest VM / Guest OS / Guest App * Hypervisor / VMM (VM Monitor) / host --- ## Type of Hypervisor ## 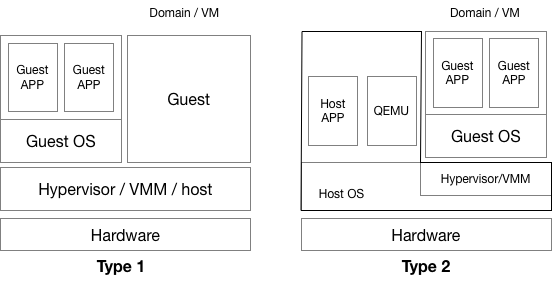 Who manages hardware? (Type-1: Hypervisor, Type-2: Host Kernel) * Type-1: Xen * Own scheduler, I/O Driver... * Type-2: Kvm * Multiplex scheduler and drivers in Linux --- # Classification and Spectrum ## Classfication - CPU Virtualization (privilege level & privileged instructions) - Memory Virtualization (GVA -> GPA -> HPA/MPA) - I/O Virtualization ## Spectrum - Traditional Full Virtualization - Para-Virtualization - Hardware-Assistant Virtualization --- ## Approach of Virtualization ## |Approach|Traditional Full Virtualization|Para-Virtualization|Hardware-assistant Virtualization<hr>| |:---|:---|:---|:---| |CPU|Binary Rewriting|Using hypercall|Root/Non-root (VT-x)<br> host mode & guest mode (AMD-v)<br> EL2 (ARM)<hr>| |Memory|Software Emluation|Shadow Page Table|Extended PT (VT-x)<br> Nested PT(AMD-v)<br> EL2 translation table (ARM)<hr>| |I/O|Software Emluation|Para / virt I/O (Front & Back-end)|Singe Root I/O Virtualization| --- ## Approach of Virtualization cont'd ## #### Software Emulation ```c /* Complete Machine Simulation */ #define REG_EAX 1; int32_t eip; int32_t regs[8]; int32_t segregs[4]; ... for (;;) { read_instruction(); switch (decode_instruction_opcode()) { case OPCODE_ADD: int src = decode_src_reg(); int dst = decode_dst_reg(); regs[dst] = regs[dst] + regs[src]; break; case .. } eip += instruction_length; } ``` --- # Type-2 Virtualization on ARMv8 # |Approach|Traditional Full Virtualization|Para-Virtualization|Hardware-assistant Virtualization<hr> | |:---|:---|:---|:---| | CPU|Binary Rewriting|Using hypercall | Root/Non-root (VT-x)<br> host mode & guest mode (AMD-v)<br> **EL2 (ARM)** <hr> | | Memory|Software Emluation | Shadow Page Table | Extended PT (VT-x)<br> Nested PT(AMD-v)<br> **EL2 translation table (ARM)** <hr> | | I/O|Software Emluation | Para / **virt I/O (Front & Back-end)** | Singe Root I/O Virtualization | --- ## Run Application ## 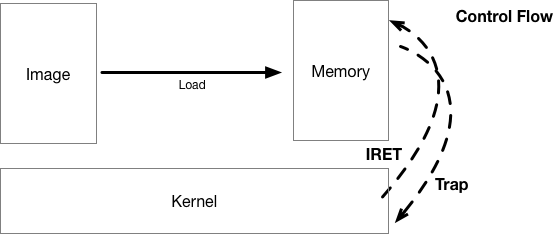 1. Load application from image to memory; 2. Give control to app; 3. App trap on privileged instructions during execution; 4. Kernel handle exception and return control; --- ## Run Guest VM ##  1. Load guest image into memory; 2. Give control to guest OS; 3. Control return to hypervisor when VMExit happen; 4. Hypervisor handle VMExit and return control using VMRun(AMD-V)/VMEnter(VT-x)/IRET(ARM); --- ## Challenges 1. Privilege instructions in guest APP traps into which level? 2. Privilege level of Guest OS? (Hypervisor has highest privilege) 3. Guest OS need physical memory. 4. I/O devices need to be shared by different VMs. --- ### CPU Virtualization - ARMv8 Virtualization Support 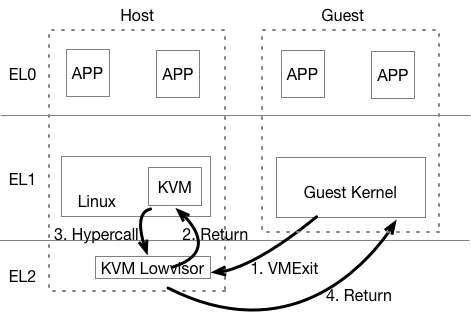 * EL2: New Exception Level for Hypervisor - Separate CPU mode designed to run hypervisor - **Not** designed to run full operating system - Reduced virtual memory support compared to EL1 - Limited support for interracting with EL0 --- ### CPU Virtualization - ARMv8 Virtualization Support #### Hypervisor Configuration Register (HCR\_EL2) * **Purpose**: Provides configuration control for virtualization, including whether various Non- secure operations are trapped to EL2.<br>HCR_EL2 is part of the Hypervisor and virtualization registers functional group. > ARM© Cortex©-A73 MPCore Processor revision: r0p2 > Technical Reference Manual > 4.3.43 Hypervisor Configuration Register --- ### CPU Virtualization cont'd $LINUX/arch/arm64/kvm/hyp/entry.S ``` ENTRY(__guest_enter) // x0: vcpu // x1: host context // x2-x17: clobbered by macros // x18: guest context // Store the host regs ... // Restore guest regs x0-x17 ldp x0, x1, [x18, #CPU_XREG_OFFSET(0)] ... // Restore guest regs x19-x29, lr restore_callee_saved_regs x18 // Restore guest reg x18 ldr x18, [x18, #CPU_XREG_OFFSET(18)] // Do not touch any register after this! eret ENDPROC(__guest_enter) ``` --- ### CPU Virtualization cont'd $LINUX/arch/arm64/kvm/hyp/entry.S ``` ENTRY(__guest_exit) // x0: return code // x1: vcpu // x2-x29,lr: vcpu regs // vcpu x0-x1 on the stack ... // Store the guest regs x2 and x3 // Retrieve the guest regs x0-x1 from the stack // Store the guest regs x0-x1 and x4-x18 // Store the guest regs x19-x29, lr get_host_ctxt x2, x3 // Now restore the host regs restore_callee_saved_regs x2 // If the exception took place, restore the EL1 exception // context so that we can report some information. msr elr_el2, x2 msr esr_el2, x3 msr spsr_el2, x4 orr x0, x0, x5 1: ret ENDPROC(__guest_exit) ``` --- ### Memory Virtualization - EL2 Translation Table 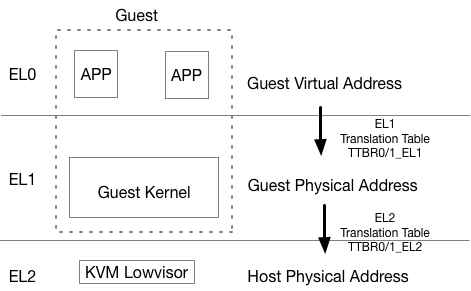 * An independant translation table in EL2 * GVA -> GPA -> HPA * VA -> IPA (Intermediate Physical Address) -> PA --- ### I/O Virtualization - virtio in QEMU 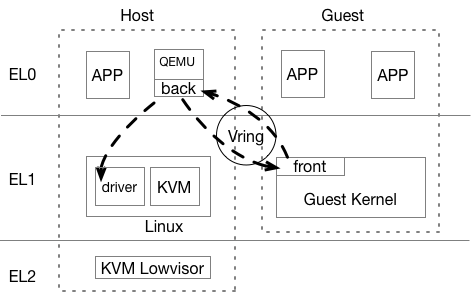 * Front-driver in guest kernel; * Back-driver in QEMU; * Transfer data via Shared-memory (Vring); * Qemu rw data using real driver; --- # Thanks #