Introduction to Virtualization 0
By SilentMing
Blog: http://silentming.net
Story Line
Brief introduction to virtualization
- (Definition, histroy …)
Classification
- (Spectrum)
Architecture on ARM (Type-2 Hypervisor)
- (It’s simple, but only cover partial)
What is Virtualization
Virtualization: A layer mapping its visible interface and resources onto the interface and resources of the underlying layer or system on which it is implemented
Abstraction – to simplify the use of the underlying resource (e.g., by removing details of the resource’s structure)
Replication – to create multiple instances of the resource (e.g., to simplify management or allocation)
Isolation – to separate the uses which clients make of the underlying resources (e.g., to improve security)
How Dose It Come ?
Run multiple OSes on a Single Computer
Histroy
- 1960: CP-40 - full virtualization
- 1970: System/370 - without virtual memory, time-sharing
- 1999: VMware Virtual Platform - x86 virtualization support
- 2003: Xen and the Art of Virtualization - Para-virtualization
- 2005: QEMU(Quick Emulator) - rescue for those times when VMware is overkill
- 2005: Free Desktop Virtualization - VMWare
- 2005 & 2006: Intel VT-x & AMD-V (Hardware support for virtualization)
- 2007: KVM(Kernel-based Virtual Machine)
- 2011: ARMv8 virtualization support
- 2013: [QEMU 1.5] ARM Cortex-A9 & Cortex-A15
- 2014: KVM/ARM & Xen 4.4
- 2017: ARMv8.4: VHE(Virtualization Host Extension)
Why Virtualization
Consolidation
- Run several different OS on a single machine
Isolation
- Keep the VMs separated as error container
- Fault tolerant
Maintenance
- Easy to deploy, backup, clone, (live) migrate
Security
- VM introspection (VMI)
- Antivirus out of the OS
Definition
The act of creating a virtual (rather than actual) version of something, including virtual computer hardware platforms, storage devices, and computer network resources. (wiki)
A layer mapping its visible interface and resources onto the interface and resources of the underlying layer or system on which it is implemented (CMU)
An enfficient, isolated duplicate of the real machine (Formal Requirements for Virtualizable Third Generation Architectures)
- Efficiency
- Innocuous instructions should execute directly on hardware
- Resource control
- Executed programs may not affect the system resources
- Equivalence
- The behavior of a program executing under the VMM should be the same as if the program were executed directly on the hardware (except possibly for timing and resource availability)
Basic Concepts
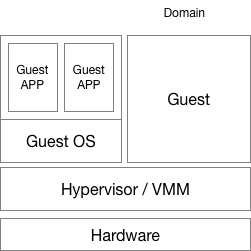
Domain/VM (Virtual Machine)
Guest VM / Guest OS / Guest App
Hypervisor / VMM (VM Monitor) / host
Type of Hypervisor
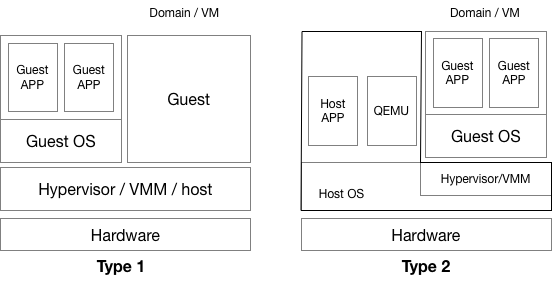
Who manages hardware? (Type-1: Hypervisor, Type-2: Host Kernel)
- Type-1: Xen
- Own scheduler, I/O Driver…
- Type-2: Kvm
- Multiplex scheduler and drivers in Linux
Classification and Spectrum
Classfication
- CPU Virtualization (privilege level & privileged instructions)
- Memory Virtualization (GVA -> GPA -> HPA/MPA)
- I/O Virtualization
Spectrum
- Traditional Full Virtualization
- Para-Virtualization
- Hardware-Assistant Virtualization
Approach of Virtualization
| Approach | Traditional Full Virtualization | Para-Virtualization | Hardware-assistant Virtualization |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Binary Rewriting | Using hypercall | Root/Non-root (VT-x) host mode & guest mode (AMD-v) EL2 (ARM) |
| Memory | Software Emluation | Shadow Page Table | Extended PT (VT-x) Nested PT(AMD-v) EL2 translation table (ARM) |
| I/O | Software Emluation | Para / virt I/O (Front & Back-end) | Singe Root I/O Virtualization |
Approach of Virtualization cont’d
Software Emulation
1 | /* Complete Machine Simulation */ |
Type-2 Virtualization on ARMv8
| Approach | Traditional Full Virtualization | Para-Virtualization | Hardware-assistant Virtualization |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Binary Rewriting | Using hypercall | Root/Non-root (VT-x) host mode & guest mode (AMD-v) EL2 (ARM) |
| Memory | Software Emluation | Shadow Page Table | Extended PT (VT-x) Nested PT(AMD-v) EL2 translation table (ARM) |
| I/O | Software Emluation | Para / virt I/O (Front & Back-end) | Singe Root I/O Virtualization |
Run Application
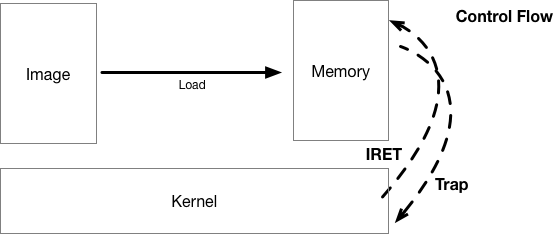
- Load application from image to memory;
- Give control to app;
- App trap on privileged instructions during execution;
- Kernel handle exception and return control;
Run Guest VM

- Load guest image into memory;
- Give control to guest OS;
- Control return to hypervisor when VMExit happen;
- Hypervisor handle VMExit and return control using VMRun(AMD-V)/VMEnter(VT-x)/IRET(ARM);
Challenges
Privilege instructions in guest APP traps into which level?
Privilege level of Guest OS? (Hypervisor has highest privilege)
Guest OS need physical memory.
I/O devices need to be shared by different VMs.
CPU Virtualization - ARMv8 Virtualization Support
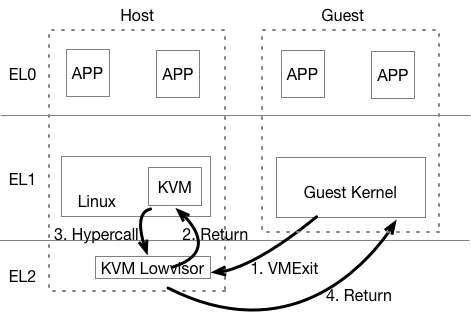
- EL2: New Exception Level for Hypervisor
- Separate CPU mode designed to run hypervisor
- Not designed to run full operating system
- Reduced virtual memory support compared to EL1
- Limited support for interracting with EL0
Hypervisor Configuration Register (HCR_EL2)
Purpose: Provides configuration control for virtualization, including whether various Non- secure operations are trapped to EL2.
HCR_EL2 is part of the Hypervisor and virtualization registers functional group.
CPU Virtualization cont’d
$LINUX/arch/arm64/kvm/hyp/entry.S
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22ENTRY(__guest_enter)
// x0: vcpu
// x1: host context
// x2-x17: clobbered by macros
// x18: guest context
// Store the host regs
...
// Restore guest regs x0-x17
ldp x0, x1, [x18, #CPU_XREG_OFFSET(0)]
...
// Restore guest regs x19-x29, lr
restore_callee_saved_regs x18
// Restore guest reg x18
ldr x18, [x18, #CPU_XREG_OFFSET(18)]
// Do not touch any register after this!
eret
ENDPROC(__guest_enter)
CPU Virtualization cont’d
$LINUX/arch/arm64/kvm/hyp/entry.S
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25ENTRY(__guest_exit)
// x0: return code
// x1: vcpu
// x2-x29,lr: vcpu regs
// vcpu x0-x1 on the stack
...
// Store the guest regs x2 and x3
// Retrieve the guest regs x0-x1 from the stack
// Store the guest regs x0-x1 and x4-x18
// Store the guest regs x19-x29, lr
get_host_ctxt x2, x3
// Now restore the host regs
restore_callee_saved_regs x2
// If the exception took place, restore the EL1 exception
// context so that we can report some information.
msr elr_el2, x2
msr esr_el2, x3
msr spsr_el2, x4
orr x0, x0, x5
1: ret
ENDPROC(__guest_exit)
Memory Virtualization - EL2 Translation Table
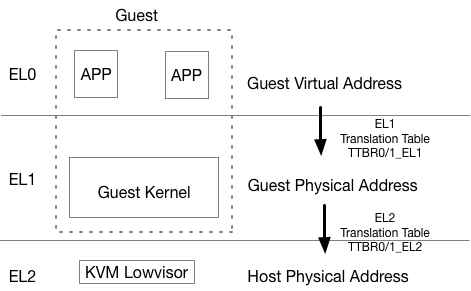
- An independant translation table in EL2
- GVA -> GPA -> HPA
- VA -> IPA (Intermediate Physical Address) -> PA
I/O Virtualization - virtio in QEMU
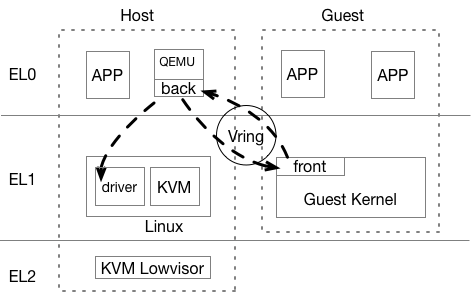
- Front-driver in guest kernel;
- Back-driver in QEMU;
- Transfer data via Shared-memory (Vring);
- Qemu rw data using real driver;

